-
1 timing of the changes
fermentative changes — изменения, возникающие при брожении
random changes — случайные изменения, случайные сдвиги
-
2 timing of the changes
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > timing of the changes
-
3 timing of the changes
Вычислительная техника: планирование изменений -
4 timing of the changes
English-Russian dictionary of computer science and programming > timing of the changes
-
5 timing
1) синхронизация; хронирование; тактирование; согласование по времени2) распределение интервалов времени; временные соотношения; временная диаграмма3) настройка выдержки ( таймера)•- job-step timing
- logic timing
- machine timing
- multiphase timing
- MUX timing
- pulse timing
- read timing
- timing of the changes
- unit delay timing
- write timing
- zero delay timingEnglish-Russian dictionary of computer science and programming > timing
-
6 man-made changes
fermentative changes — изменения, возникающие при брожении
English-Russian dictionary on nuclear energy > man-made changes
-
7 precipitous changes
fermentative changes — изменения, возникающие при брожении
English-Russian dictionary on nuclear energy > precipitous changes
-
8 purchase timing
марк. выбор времени покупки (принятие покупателем решения о том, когда совершить покупку)to research purchase timing behavior in two related product categories — изучать принятие решений потребителями о времени совершения покупки для двух категорих продуктов
In other cases, sales promotion may result only in changes in purchase timing among brand loyals, who may take advantage of a good deal and then stockpile the product in the home for future use.
A consumer demand model, which will consist of sub-models aimed at predicting brand choice and the purchase timing of customers.
See: -
9 планирование изменений
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > планирование изменений
-
10 function Ah
функция Ah (реле времени)
Задержка импульса при каждой подаче напряжения на управляющий вход.
[Интент]EN
function Ah
Pulse delayed relay (single cycle) with control signal.
[Schneider Electric]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
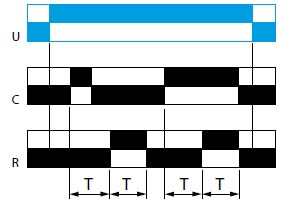
Function Ah
Pulse delayed relay (single cycle) with control signal
After power-up, pulsing or maintaining control contact C starts the timing T. A single cycle then starts with 2 timing periods T of equal duration (start with output in rest position).
Output R changes state at the end of the first timing period T and reverts to its initial position at the end of the second timing period T.
Control contact C must be reset in order to re-start the single flashing cycle.
[Schneider Electric]
Function Ah
Flashing single cycle by switch (not resettable)
After power-up, pressing or holding down the switch starts timing. At the end of timing, the output is energised. At the end of this second timing, the output falls back to its initial value.
[Crouzed]Функция Ah
Задержка импульса при каждой подаче напряжения на управляющий вход
После подачи питания на реле и последующей подачи импульса или постоянно напряжения на управляющий вход С выполняется отсчет паузы длительностью T, а затем такой же длительности импульса. По окончании паузы Т выход реле R замыкается, а по окончании длительности импульса - возвращается в исходное состояние.
Для возобновления такого же цикла формирования одного импульса необходимо вновь подать напряжение на управляющий вход.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > function Ah
-
11 change
tʃeɪndʒ
1. сущ.
1) а) перемена;
изменение, сдвиг( from, into, to, in, of) ;
замена (любого рода, напр., игрока в футболе) ;
череда, чередование to bring about, effect, make a change ≈ внести изменения to undergo change ≈ подвергаться изменениям, претерпевать изменения drastic, great change ≈ большие перемены little change ≈ незначительная модификация marked change ≈ значительные перемены momentous change ≈ мгновенные изменения needed change ≈ необходимые изменения quick change ≈ быстрые изменения radical, striking, sweeping change ≈ радикальные перемены sudden change ≈ внезапные изменения, внезапный сдвиг welcome change ≈ желанные перемены Change, constant change, is the law of organic life. ≈ Изменение, вечное непрекращающееся изменение - закон органической жизни. There was little change in his condition. ≈ Его состояние не изменилось. a change occurs, takes place ≈ происходит изменение a change for the better ≈ изменение к лучшему the change from spring to summer ≈ переход от весны к лету (смена времен года) changes in personnel ≈ кадровые изменения the change of seasons ≈ смена времен года б) перен. смерть I went to my mother, and found her change was near. ≈ Я проведал мать и понял, что ей недолго осталось. в) муз. вариация;
модуляция ∙ social change change of pace change of air change of life for a change
2) что-л. взамен чего-л. другого а) смена (белья, платья) б) сдача;
мелкие деньги, мелочь to count, get, take one's change ≈ получить сдачу to give, make, return change for ≈ дать сдачу мелочью to keep the change ≈ оставить сдачу Сan you give me change for a pound? ≈ У Вас будет сдача с фунта? Passengers are requested to examine their tickets and change before leaving. ≈ Пассажиров просят проверять билеты и сдачу не отходя от кассы. small change no change given make change в) пересадка( на железной дороге, трамвае) г) авт. включение другой передачи, переключение передач, скоростей - change down - change up д) расплата, "должное";
возврат долга He gave me a real change, helped my son into University. ≈ Он мне оказал большую услугу - помог моему сыну поступить. not to get any change from smb. Take your change out of that! ≈ Вот тебе! Это тебе за то-то и то-то! (реплика в драке, в момент совершения мести и т.п.) ∙ change of heart hunt change
3) новолуние I still have fits, always with a change in the moon. ≈ У меня до сих пор на новолуние случаются припадки.
4) мн. а) отступление от канонического порядка колокольного звона (от самого большого колокола к самому маленькому) б) тот или иной тип колокольного звона (любой порядок колоколов) Four bells admit twenty-four changes in ringing. ≈ Для четырех колоколов возможно двадцать четыре типа звонов. в) та или иная манера игры на колоколах ∙ ring the changes
5) (Change) (лондонская) биржа (можно рассматривать как сокр. от Exchange, что, впрочем, этимологически неверно) Good, honest, generous men at home, will be wolves and foxes on change! ≈ Дома они сущие ангелы, честные до мозга костей, но на бирже они кровожадные волки и хитрые лисы!
6) шотл. пивная ∙ to get no change out of smb. разг. ≈ ничего не добиться от кого-л. to take the change on smb. разг. ≈ обмануть кого-л.
2. гл.
1) менять(ся), изменять(ся) ;
заменять, сменять School has changed the boy into a coward. ≈ Школа сделала его трусом. I am the Lord, I change not. ≈ Ибо Я - Господь, Я не изменяюсь ( Мал 3,
6.) Nothing will die, all things will change. ≈ Ничто не умирает, но все меняется (Лаун-Теннисон) - change colour change countenance change hands change to change into change for the better change for the worse Syn: alter, convert, modify, transfigure, transform, transmogrify, transmute, render Ant: maintain, stabilize, sustain
4)
2) заменять одно на другое а) переодеваться;
одеваться к ужину, надевать вечернее платье to change from, change out of ≈ снимать что-л. I shall have to change from (или out of) these wet clothes. ≈ Мне надо переодеться, я весь мокрый. to change into ≈ надевать что-л. Syn: to change oneself б) делать пересадку, пересаживаться( на другой поезд, трамвай и т. п.) (to) all change! ≈ пересадка! в) менять, обменивать (о деньгах) I should like to change these pounds into dollars. ≈ Мне нужно обменять фунты на доллары. г) меняться, обмениваться( чем-л.) I'd like to change this dress for one in a larger size. ≈ Я бы хотел обменять это платье на такое же, но большего размера. д) авт. переключать передачу - change up - change down е) переходить в другую фазу (о луне) ж) переезжать, менять местожительство, место работы If a vicar dies or changes. ≈ Если викарий умрет или будет переведен на другую кафедру. ∙ change bandage - change one's mind change sides Syn: substitute, replace, exchange, interchange
3) изменяться до полной неузнаваемости, менять сущность а) скисать;
сгнить;
портиться б) превращаться ∙ change back change from change into change down change over change round change up change with to change horses in the midstream ≈ "менять коней на переправе", производить крупные перемены в критический или опасный момент перемена, изменение;
- * of weather перемена погоды;
- * of scene перемена обстановки;
- * of the scenes (театроведение) перемена декораций;
- * of heart изменение намерений;
переворот в убеждениях или чувствах;
- * of pace смена ритма, скорости, хода;
резкая смена образа жизни и деятельности;
внесение разнообразия в жизнь;
- * of front( военное) перемена фронта;
коренные изменения;
поворот на 180 градусов;
- * of air перемена обстановки;
(техническое) обмен воздуха;
- * of station( военное) командировка, перевод в другую часть;
- * of leads перемена ноги на галопе;
- * of tide чередование приливно-отливных течений;
- subject to * могущий измениться;
подлежащий изменению;
- many *s have taken place многое изменилось;
- the * from winter to spring переход от зимы к весне;
- * gear (техническое) механизм изменения хода и скоростей;
- * part (техническое) сменная деталь;
- * switch( техническое) переключатель замена, смена;
подмена;
разнообразие;
- for a * для разнообразия;
- you need a * вам нужно переменить обстановку;
- this journey will be a * for you поездка внесет в вашу жизнь некоторое разнообразие смена (белья) ;
- * station( военное) пункт обмена обмундирования;
- a * of underwear смена белья размен (денег) ;
- to give * for a pound note разменять банковый билет в 1 фунт стерлингов обмен (на другую валюту) сдача;
- he got ninepence * он получил 9 пенсов сдачи;
- keep the *! сдачи не нужно разменная монета;
мелкие деньги, мелочь;
что-л мелкое;
пустяки, мелочи жизни пересадка ( на железной дороги) ;
- no * for Oxford до Оксфорда без пересадки;
(здесь) пересадки на Оксфорд нет;
- to make a * at N. делать пересадку в N. (специальное) превращение;
- chemical * химическое превращение (астрономия) новая фаза Луны, новолуние обыкн. pl трезвон( колоколов) - to ring the *s вызванивать на колоколах (шотландское) кабачок, пивная "параграф" (фигурное катание) > to get no * out of smb. ничего не добиться от кого-л;
ничего не выведать у кого-л;
> to take the * out of smb. отомстить кому-л;
> take your * out of that! получайте!, вот вам!;
> to ring the * повторять, твердить на все лады одно и то же;
быстро менять одежду и внешний вид;
переодеваться, маскироваться;
менять, изменять;
переделывать;
- to * the course( морское) изменять курс;
- to * one's address переменить адрес, переехать;
- to * colour покраснеть или побледнеть;
- to * countenance измениться в лице;
- to * step сменить ногу;
- * arms!( военное) передать оружие! (из одной руки в другую, с одного плеча на другое) - success *d him добившись успеха, он изменился;
- we can't * human nature человеческую природу не переделаешь;
- we *d the room by making a new window мы перестроили комнату, прорезав новое окно меняться, изменяться;
- the weather *s very often погода часто меняется;
- times * времена меняются;
- the wind has *d from north to east северный ветер перешел в восточный;
- how he has *d как он изменился! - they are changing from their old ideas они отказываются от своих старых представлений;
- I could not wish it *d я бы хотел, чтобы все оставалось по-прежнему обменивать;
- take the hat back to the shop and * it отнеси шляпу в магазин и поменяй ее обмениваться, меняться;
поменяться с кем-л местами переодеваться;
- to * for dinner переодеться к обеду;
- to * into a new suit переодеться в новый костюм;
- he *d his clothes он переоделся;
менять белье, пеленки;
- to * a bed перестелить постель, сменить постельное белье;
- to * a baby (разговорное) перепеленать ребенка превращать;
- the magician *d a watch into a rabbit фокусник превратил часы в кролика превращаться;
- caterpillars * into butterflies гусеницы превращаются в бабочек;
- to * into a bird превратиться в птицу, обернуться птицей;
- to * into a miser превратиться в скрягу, стать скрягой портиться;
- this colour *s эта краска линяет( разговорное) портить;
- the milk is *d молоко свернулось переходить в новую фазу (о луне) ;
- the moon will * on the fourteenth новолуние наступит четырнадцатого разменивать, менять ( деньги) ;
- to * a pound note разменять банковый билет в один фунт;
- to * a cheque получить наличные деньги по чеку обменивать (другую валюту) ;
- to * pounds into francs обменять фунты на франки делать пересадку, пересаживаться;
- to * from one train to another пересаживаться на другой поезд;
- all*! поезд дальше не идет! > to * one's mind передумать, изменить свое решение;
> to * hands переходить из рук в руки;
переходить к другому владельцу;
> the house has *d hands four times дом переходил от владельца к владельцу четыре раза;
> to * the hand переменить направление (конный спорт) ;
> to * one's skin измениться до неузнаваемости;
"перекраситься";
> to * face повернуться на 180 градусов, переменить фронт, повернуться в другую сторону;
> to * sides перебежать в лагерь противника;
изменить своим убеждениям;
> to * one's note переменить тон, заговорить по-иному;
> to * horses in midstream производить крупные перемены в опасный момент;
менять лошадей на переправе address ~ вчт. изменение адреса address ~ вчт. переадресация administrative ~ административная реорганизация ~ делать пересадку, пересаживаться (to - на другой поезд, трамвай и т. п.) ;
all change! пересадка! change биржа ~ делать пересадку, пересаживаться (to - на другой поезд, трамвай и т. п.) ;
all change! пересадка! ~ делать пересадку ~ замена ~ изменение ~ изменять Change (сокр. от Exchange) лондонская биржа ~ мелкие деньги ~ мелочь ~ менять(-ся), изменять(ся) ;
сменять, заменять;
times change времена меняются ~ менять ~ менять деньги ~ новая фаза Луны, новолуние ~ обменивать(ся) ~ обменивать ~ переделывать ~ перемена;
изменение;
сдвиг;
social change общественные (или социальные) сдвиги ~ перемена ~ переодеваться ~ пересадка (на железной дороге, трамвае) ;
no change for Oxford в Оксфорд без пересадки ~ пересадка ~ to ~ up (down) авто переходить на большую (меньшую) скорость ~ подмена ~ размен (денег) ~ размен денег ~ разменная монета, сдача ~ разменная монета ~ разменять (деньги) ~ разнообразие;
for a change для разнообразия ~ разнообразие ~ сдача;
мелкие деньги, мелочь ~ сдача ~ скисать, прокисать;
портиться ~ смена (белья, платья) ~ смена ~ (обыкн. pl) трезвон, перезвон колоколов to ~ colour покраснеть или побледнеть to ~ countenance измениться в лице ~ for reasons of consistency изменение из соображений совместимости ~ gear тех. механизм перемены направления движения to ~ hands переходить из рук в руки;
переходить к другому владельцу hands: hands: change ~ переходить в другие руки to ~ horses in the midstream производить крупные перемены в критический или опасный момент ~ in behaviour изменение поведения ~ in cash value изменение стоимости в денежном выражении ~ in currency exchange rate изменение валютного курса ~ in currency exchange rate изменение обменного курса ~ in cyclical trend полит.эк. изменение периодического тренда ~ in definition изменение формулировки ~ in direction перемена курса ~ in exchange rates изменение валютных курсов ~ in foreign reserves изменение валютных запасов ~ in interest rates изменение процентных ставок ~ in inventories изменение уровней запасов ~ in net foreign reserves изменение чистой суммы валютных резервов ~ in net forward sales бирж. изменение объема нетто-продаж на срок ~ in order of priorities изменения порядка очередности ~ in practice изменение процедуры ~ in presentation of accounts изменение порядка представления отчетности ~ in price изменение цен ~ in statistical recording изменение статистической отчетности ~ in stock изменение уровня запасов ~ in stockbuilding изменение порядка создания запасов ~ in timing изменение чередования периодов ~ in work in progress изменение выполняемой работы ~ of address изменение адреса ~ of address модификация адреса ~ of address переадресование ~ of air тех. обмен воздуха ~ of air перемена обстановки ~ of attitude изменение отношения ~ of government смена правительства ~ of level изменение уровня ~ of life мед. климактерий ~ of managers смена руководителей ~ of name изменение названия ~ of ownership раздел собственности ~ of policy-orientation изменение политической ориентации ~ of profession смена профессии ~ of supplier смена поставщика ~ of system изменение системы ~ of trade смена профессии to ~ one's mind передумать, изменить решение mind: to be of the same ~ оставаться при своем мнении;
to speak one's mind говорить откровенно;
to change (или to alter) one's mind передумать;
to my mind по моему мнению ~ over меняться местами ~ over вчт. переключать ~ over переходить (to - на что-л.) to ~ sides перейти на другую сторону (в политике, в споре и т. п.) sides: sides: change ~ изменять точку зрения control ~ вчт. смена режима управления de facto ~ фактическое изменение engineering ~ вчт. техническое изменение exact ~ точное изменение exchange rate ~ изменение валютного курса fee ~ изменение размера сбора ~ разнообразие;
for a change для разнообразия generational ~ смена поколений to get no ~ out (of smb.) разг. ничего не добиться (от кого-л.) job ~ продвижение по службе minor ~ незначительное изменение ~ пересадка (на железной дороге, трамвае) ;
no change for Oxford в Оксфорд без пересадки postproduction ~ вчт. доработка в процессе изготовления price ~ нетто-изменение курса ценной бумаги в течение рабочего дня price ~ переоценка public ~ вчт. общедоступное изменение random ~s случайные изменения to ring the changes (on) повторять, твердить на все лады одно и то же runtime ~ вчт. изменение на период прогона small ~ мелкая разменная монета small ~ мелкие деньги, мелочь small ~ (что-л.) мелкое, незначительное small ~ небольшое изменение small ~ незначительное изменение small ~ несущественное изменение ~ перемена;
изменение;
сдвиг;
social change общественные (или социальные) сдвиги social ~ изменения в обществе social ~ социальная перемена (перемены в жизни общества) step ~ вчт. ступенчатое изменение structural ~ структурное изменение to take the ~ (on smb.) разг. обмануть (кого-л.) to take the ~ out of a person разг. отомстить (кому-л.) ~ менять(-ся), изменять(ся) ;
сменять, заменять;
times change времена меняются -
12 change
[tʃeɪndʒ]address change вчт. изменение адреса address change вчт. переадресация administrative change административная реорганизация change делать пересадку, пересаживаться (to - на другой поезд, трамвай и т. п.); all change! пересадка! change биржа change делать пересадку, пересаживаться (to - на другой поезд, трамвай и т. п.); all change! пересадка! change делать пересадку change замена change изменение change изменять Change (сокр. от Exchange) лондонская биржа change мелкие деньги change мелочь change менять(-ся), изменять(ся); сменять, заменять; times change времена меняются change менять change менять деньги change новая фаза Луны, новолуние change обменивать(ся) change обменивать change переделывать change перемена; изменение; сдвиг; social change общественные (или социальные) сдвиги change перемена change переодеваться change пересадка (на железной дороге, трамвае); no change for Oxford в Оксфорд без пересадки change пересадка change to change up (down) авто переходить на большую (меньшую) скорость change подмена change размен (денег) change размен денег change разменная монета, сдача change разменная монета change разменять (деньги) change разнообразие; for a change для разнообразия change разнообразие change сдача; мелкие деньги, мелочь change сдача change скисать, прокисать; портиться change смена (белья, платья) change смена change (обыкн. pl) трезвон, перезвон колоколов to change colour покраснеть или побледнеть to change countenance измениться в лице change for reasons of consistency изменение из соображений совместимости change gear тех. механизм перемены направления движения to change hands переходить из рук в руки; переходить к другому владельцу hands: hands: change change переходить в другие руки to change horses in the midstream производить крупные перемены в критический или опасный момент change in behaviour изменение поведения change in cash value изменение стоимости в денежном выражении change in currency exchange rate изменение валютного курса change in currency exchange rate изменение обменного курса change in cyclical trend полит.эк. изменение периодического тренда change in definition изменение формулировки change in direction перемена курса change in exchange rates изменение валютных курсов change in foreign reserves изменение валютных запасов change in interest rates изменение процентных ставок change in inventories изменение уровней запасов change in net foreign reserves изменение чистой суммы валютных резервов change in net forward sales бирж. изменение объема нетто-продаж на срок change in order of priorities изменения порядка очередности change in practice изменение процедуры change in presentation of accounts изменение порядка представления отчетности change in price изменение цен change in statistical recording изменение статистической отчетности change in stock изменение уровня запасов change in stockbuilding изменение порядка создания запасов change in timing изменение чередования периодов change in work in progress изменение выполняемой работы change of address изменение адреса change of address модификация адреса change of address переадресование change of air тех. обмен воздуха change of air перемена обстановки change of attitude изменение отношения change of government смена правительства change of level изменение уровня change of life мед. климактерий change of managers смена руководителей change of name изменение названия change of ownership раздел собственности change of policy-orientation изменение политической ориентации change of profession смена профессии change of supplier смена поставщика change of system изменение системы change of trade смена профессии to change one's mind передумать, изменить решение mind: to be of the same change оставаться при своем мнении; to speak one's mind говорить откровенно; to change (или to alter) one's mind передумать; to my mind по моему мнению change over меняться местами change over вчт. переключать change over переходить (to - на что-л.) to change sides перейти на другую сторону (в политике, в споре и т. п.) sides: sides: change change изменять точку зрения control change вчт. смена режима управления de facto change фактическое изменение engineering change вчт. техническое изменение exact change точное изменение exchange rate change изменение валютного курса fee change изменение размера сбора change разнообразие; for a change для разнообразия generational change смена поколений to get no change out (of smb.) разг. ничего не добиться (от кого-л.) job change продвижение по службе minor change незначительное изменение change пересадка (на железной дороге, трамвае); no change for Oxford в Оксфорд без пересадки postproduction change вчт. доработка в процессе изготовления price change нетто-изменение курса ценной бумаги в течение рабочего дня price change переоценка public change вчт. общедоступное изменение random changes случайные изменения to ring the changes (on) повторять, твердить на все лады одно и то же runtime change вчт. изменение на период прогона small change мелкая разменная монета small change мелкие деньги, мелочь small change (что-л.) мелкое, незначительное small change небольшое изменение small change незначительное изменение small change несущественное изменение change перемена; изменение; сдвиг; social change общественные (или социальные) сдвиги social change изменения в обществе social change социальная перемена (перемены в жизни общества) step change вчт. ступенчатое изменение structural change структурное изменение to take the change (on smb.) разг. обмануть (кого-л.) to take the change out of a person разг. отомстить (кому-л.) change менять(-ся), изменять(ся); сменять, заменять; times change времена меняются -
13 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.———————————————————————————————————————— -
14 function A
функция A (реле времени)
задержка срабатывания при подаче питания
[Интент]EN
function A
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
delay on energisation
[Crouzed]
function A
power on delay relay
[Schneider Electric]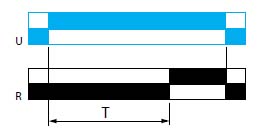
The timing period T begins on energization.
After timing, the output R close.
[Schneider Electric]Отсчет выдержки времени T начинается от момента подачи питания на реле времени.
По окончании выдержки T выход R замыкается.
[Перевод Интент]Single timing cycle which begins on energisation.
The output changes state after timing.
[Crouzed]Однократный отсчет выдержки времени, начинающийся от момента подачи питания на реле времени.
Выход реле изменяет свое состояние после окончания выдержки времени
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > function A
15 function Ac
функция Ac (реле времени)
- Отсчет двух выдержек времени: после подачи и после снятия напряжения с управляющего входа.
- Задержка срабатывания и задержка возврата реле после подачи и после снятия напряжения с управляющего входа.
[Интент]EN
function Ac
Timing after closing and opening of control contact
[Crouzed]
function Ac
On-delay and off-delay relay with control signal
[Schneider Electric]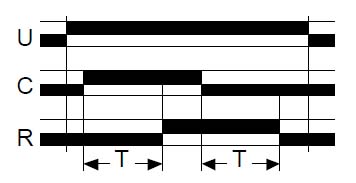
Рис. CrouzedПараллельные тексты EN-RU
After energisation, closure of the control contact causes the timing period T to commence and output relay R (or the load) changes state at the end of this interval.
When contact C (Y1) opens, relay R resets after a second timing period T.
[Crouzed]После подачи питания на реле и последующего замыкания контакта в цепи управляющего входа выполняется отсчет выдержки времени Т, по окончании которого выходное реле R (или нагрузка) изменяет свое состояние.
После размыкания контакта С еще раз отсчитывается выдержка времени Т, по окончании которой реле R возвращается в исходное состояние.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > function Ac
См. также в других словарях:
Timing margin — is an expression of the difference between the actual change in a signal and the latest time at which the signal can change in order for the circuit to function correctly. It is used in the design of digital electronics.In this image, the lower… … Wikipedia
The Autobiography of Malcolm X — The Autobiography of Malcolm X First edition … Wikipedia
The God Makers II — is an anti Mormon movie produced by Ed Decker and Jeremiah Films. The film claims to be an exposé of secrets of the Mormon Church. The film is a followup to Decker’s earlier film The God Makers .Overview of the filmIntroductionThe introductory… … Wikipedia
The Legend of Dragoon — North American box art Developer(s) SCEI Publisher(s) … Wikipedia
The Fiver — is a notable and humorous daily football email published by the Guardian Unlimited website. It is delivered to subscribers’ inboxes at (approximately) 5 p.m. Monday – Friday (hence the name Fiver ) but does not appear in the print edition of the… … Wikipedia
The Wizard of Oz (1939 film) — The Wizard of Oz Theatrical release poster Directed by Victor Fleming Uncredited: Norman Taurog Richard Thorpe … Wikipedia
The World of Kong — The World of Kong: A Natural History of Skull Island is a 2005 encyclopedic book, made for the release of Peter Jackson s King Kong. The book tells all about King Kong s fictional world. It talks about everything on Skull Island, from the… … Wikipedia
The Bill title sequences — The Bill s title sequences have varied greatly over the show s 23 years on air.Opening CreditsThe first series in 1984 has its own unique title sequence, featuring images of the feet of two uniformed officers walking towards the camera… … Wikipedia
The Superinvestors of Graham-and-Doddsville — is an article by Warren Buffett promoting value investing, published in the Fall, 1984 issue of Hermes , Columbia Business School magazine. It was based on a speech given on May 17, 1984 at the Columbia University School of Business in honor of… … Wikipedia
Timing attack — In cryptography, a timing attack is a side channel attack in which the attacker attempts to compromise a cryptosystem by analyzing the time taken to execute cryptographic algorithms. The attack exploits the fact that every operation in a computer … Wikipedia
The Book of Five Rings — Go Rin No Sho calligraphed in Kanji . Musashi strived for as great a mastery in that art as in swordsmanship. The Book of Five Rings (五輪書, Go Rin No Sho … Wikipedia
Перевод: с английского на русский
с русского на английский- С русского на:
- Английский
- С английского на:
- Все языки
- Немецкий
- Русский
